Type 2 Diabetes (DM2) is a complex metabolic disease, characterized by adipose and muscle insulin resistance accompanied by defects in pancreatic insulin secretion or loss of function of insulin-secreting cells. Present therapeutic modalities include lifestyle modification and pharmaceutical agents, however many patients fail to achieve blood glucose homeostasis.
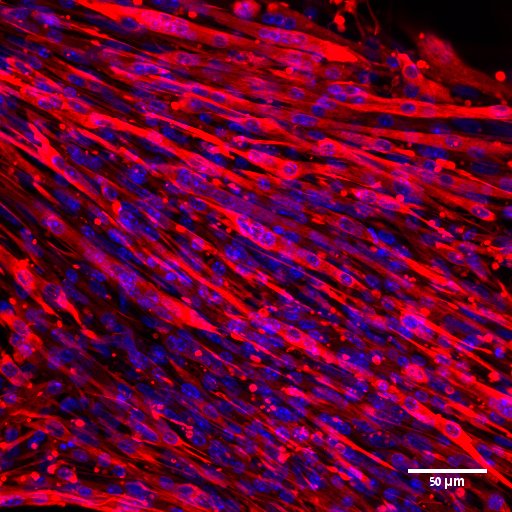
This research proposes to overcome peripheral tissue insulin resistance by genetically modifying skeletal muscle cells and use them to construct engineered muscle tissue. Upon implantation of such engineered muscle, overall glucose uptake of the animal is expected to be enhanced, therefore improving diabetic state.
This study is supported by the The Rina and Avner Schneur Center of Diabetes Research (http://schneur-diabetic-center.net.technion.ac.il/)